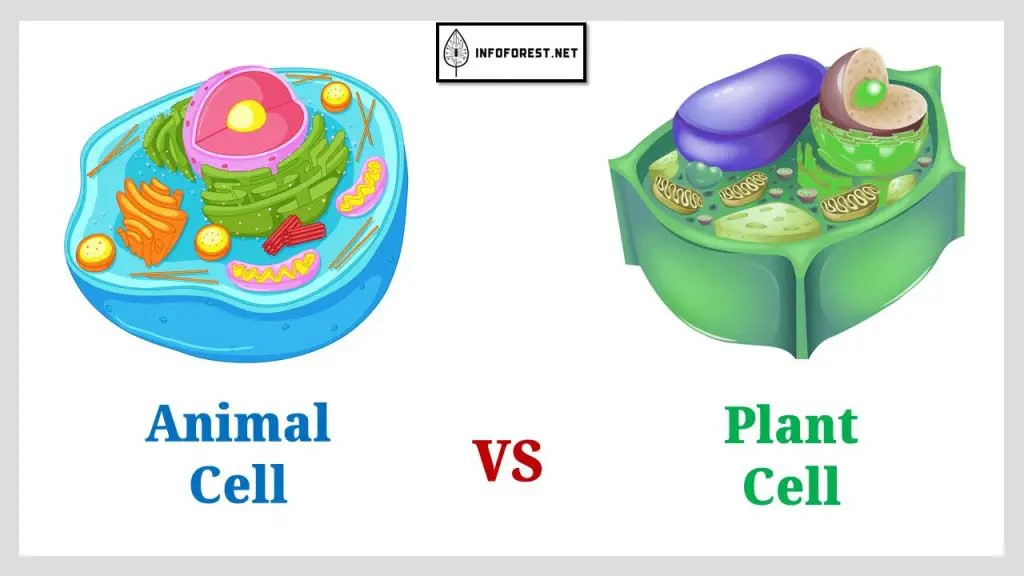
Plant cells and animal cells are the two main types of eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. While there are many similarities between these two types of cells, there are also several key differences that reflect the unique functions and adaptations of plants and animals. In this article, we are going to analyze Plant Cell vs Animal cell, or in other words, the differences between plant cells and animal cells.
One of the most notable differences between plant cells and animal cells is the presence of a cell wall in plant cells. The cell wall is a rigid, semi-permeable layer that surrounds the cell membrane and provides additional support and protection for the cell. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
Another difference is the presence of chloroplasts in plant cells. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
Plant cells also have larger central vacuoles, which are fluid-filled organelles that store water and other substances. In contrast, animal cells have smaller, less prominent vacuoles.
There are other differences as well, such as the presence of plasmodesmata in plant cells (small channels that allow for communication between cells) and the lack of lysosomes in plant cells (organelles that contain enzymes involved in digestion).
What is Plant Cell
A plant cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that is found in plants. It is characterized by the presence of a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. Like all eukaryotic cells, plant cells also have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
The main components of a plant cell are:
- Cell wall: a rigid, semi-permeable layer that surrounds the cell membrane and provides additional support and protection for the cell.
- Cell membrane: a thin, semi-permeable barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside of the cell from the external environment.
- Cytoplasm: a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the organelles.
- Nucleus: a large organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell’s activities.
- Chloroplasts: organelles that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis.
- Mitochondria: organelles that produce energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus: organelles involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins and lipids.
- Central vacuole: a large, fluid-filled organelle that stores water and other substances.
The size of plant cells can vary widely depending on the type of plant and the specific function of the cell. For example, cells in the leaves of a plant may be larger and contain more chloroplasts than cells in the roots. However, in general, plant cells are typically larger than animal cells.
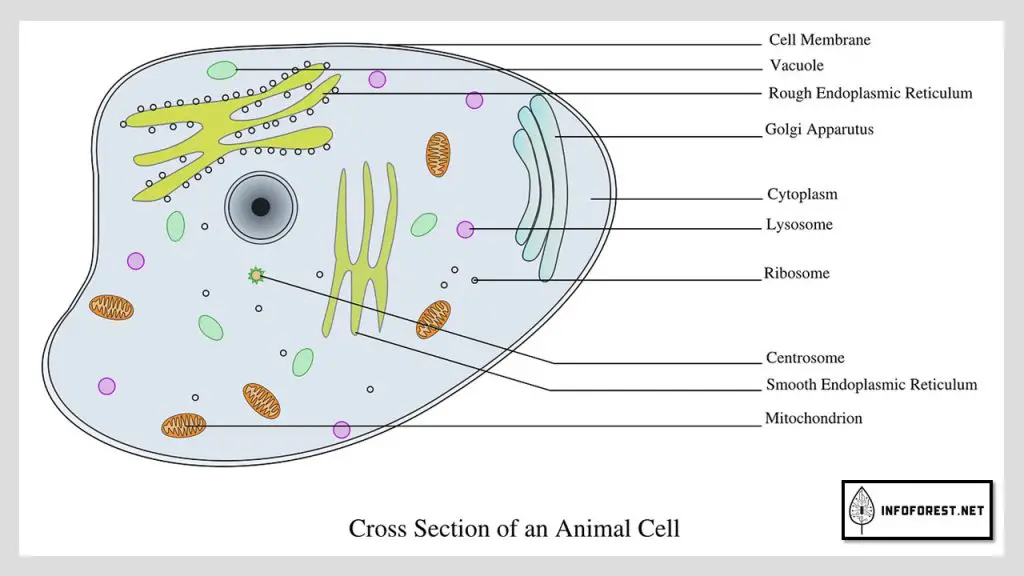
What is Animal Cell
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that is found in animals. It is characterized by the absence of a cell wall and chloroplasts, and the presence of smaller, less prominent vacuoles. Like all eukaryotic cells, animal cells have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
The main components of an animal cell are:
- Cell membrane: a thin, semi-permeable barrier that surrounds the cell and separates the inside of the cell from the external environment.
- Cytoplasm: a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the organelles.
- Nucleus: a large organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell’s activities.
- Mitochondria: organelles that produce energy for the cell through a process called cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and Golgi apparatus: organelles involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins and lipids.
- Vacuoles: small, fluid-filled organelles that store water and other substances.
The size of animal cells can vary widely depending on the type of animal and the specific function of the cell. However, in general, animal cells are typically smaller than plant cells.
The main differences between Plant cell and animal cell
there are several key differences between plant cells and animal cells:
- Cell wall: Plant cells have a cell wall, which is a rigid, semi-permeable layer that surrounds the cell membrane and provides additional support and protection for the cell. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
- Chloroplasts: Plant cells have chloroplasts, which are organelles that contain chlorophyll and are responsible for photosynthesis. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
- Vacuoles: Plant cells have larger central vacuoles, which are fluid-filled organelles that store water and other substances. Animal cells have smaller, less prominent vacuoles.
- Plasmodesmata: Plant cells have plasmodesmata, which are small channels that allow for communication between cells. Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata.
- Lysosomes: Animal cells have lysosomes, which are organelles that contain enzymes involved in digestion. Plant cells do not have lysosomes.
Examples of Plant Cell vs Animal Cell
- A cell wall helps a plant cell maintain its shape and support the plant, while an animal cell does not have this support and may change shape easily.
- Chloroplasts allow a plant cell to produce its own energy through photosynthesis, while an animal cell must obtain energy from other sources.
- A central vacuole in a plant cell helps the plant store water and maintain its turgidity (rigidity due to water pressure), while an animal cell does not have this ability.
- Plasmodesmata allow for communication between plant cells, enabling the plant to coordinate activities such as growth and response to stimuli. Animal cells do not have this ability.
- Lysosomes in animal cells allow for the digestion of materials such as food particles and waste products, while plant cells do not have this function.
Most Viewed Articles
Conclusion
In conclusion, plant cells and animal cells are both types of eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. However, there are several key differences between these two types of cells that reflect the unique functions and adaptations of plants and animals. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuoles, while animal cells do not. Animal cells have lysosomes, while plant cells do not. These differences allow plant cells and animal cells to perform the specific functions necessary for the survival and growth of plants and animals.
We also invite you not to miss our other popular articles such as:
Plant Cell vs Animal Cell – Difference between left and right Twix–Difference Between Eastern Time Zone and Central Time Zone–Difference Between Capitalism and Communism– Difference Between EST and EDT–How many weeks in a Year– Difference Between Evening and Afternoon – Democrat vs Republican – Kilometer vs Mile– Catholicism vs Christianity and Difference Between Zip Code and Postal Code